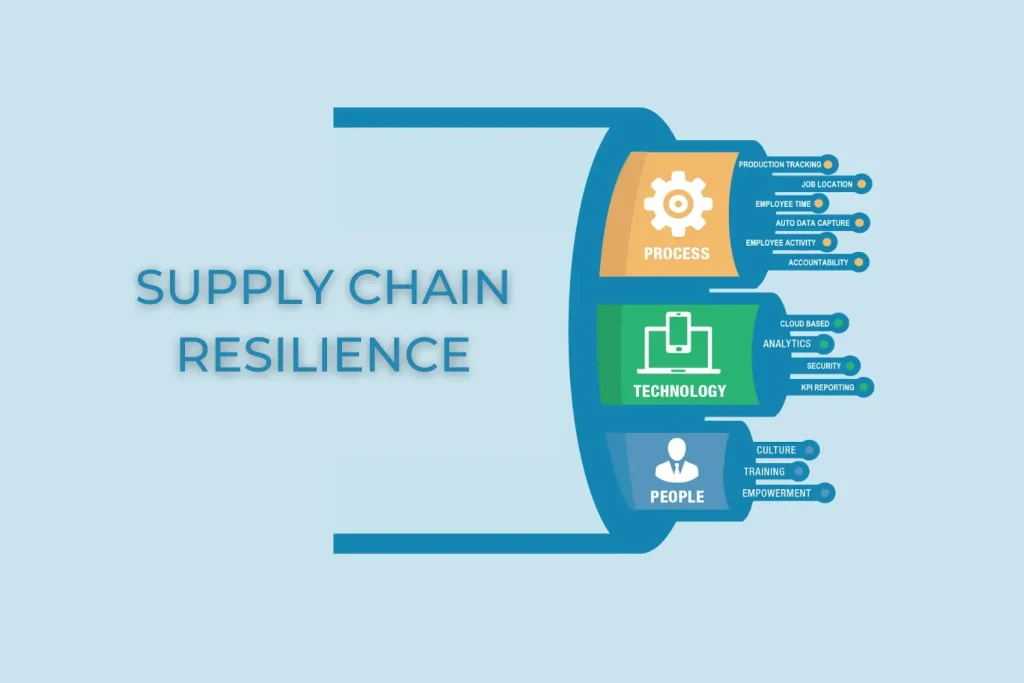
Supply chain resilience is the backbone of reliable delivery in today’s interconnected economy, where seamless flows power everyday products and services, from groceries to gadgets, across a dense web of suppliers, manufacturers, and carriers. As businesses navigate global supply chains, risk management in supply chains becomes integral to anticipating disruptions and preserving customer trust, guiding investments in redundancy, supplier diversification, and data-driven decision making. When disruptions strike, resilient networks draw on enhanced visibility, redundant options, and agile sourcing to minimize impact on service levels and costs while maintaining quality. From climate events to geopolitical shifts, resilience strategies in supply chains help firms stay competitive in a modern economy logistics landscape, enabling faster recovery and smoother customer experiences even when shocks unfold. By combining proactive planning with rapid execution, organizations build operations that absorb shocks and recover quickly, protecting revenue and reputation while supporting sustainable growth.
From an LSI perspective, the topic translates into network robustness, supply network agility, and continuity of operations across procurement, production, and distribution. Industry voices describe disruption readiness, resilience-enabling governance, and collaborative risk management as core capabilities that keep value flowing under stress. The emphasis shifts from ultra-lean efficiency to a balanced mix of redundancy, visibility, and flexible capacity within global value chains. Practically, firms build this posture through better data sharing, scenario planning, supplier collaboration, and diversified logistics options that preserve service levels during shocks.
Supply chain resilience: integrating risk management in supply chains and resilience strategies in supply chains for the modern economy
Supply chain resilience is built on preparedness, visibility, and speed. By embedding risk management in supply chains into planning, firms map vulnerabilities, quantify exposure, and design contingency actions that can be mobilized rapidly. In the era of global supply chains, disruptions are not if but when, making supply chain disruption scenarios a routine part of budgeting and strategy. The lens of modern economy logistics shows how interconnected routes, modes, and carriers must be coordinated to prevent minor perturbations from becoming material performance drag.
Proactive resilience strategies in supply chains require end-to-end visibility, diversified sourcing, and modular design. Real-time data, digital twins, and AI-enabled analytics help teams anticipate bottlenecks and accelerate recovery. When disruptions occur, firms with robust resilience strategies in supply chains can reroute shipments, switch suppliers, and adjust inventories without sacrificing service levels. The goal is not perfect predictability but rapid response and continuous improvement across the network.
Global supply chains in the modern economy: strengthening resilience through risk management and agile logistics
Global supply chains carry unprecedented scale and complexity, which magnifies exposure to geopolitical shifts, climate risks, and cyber threats. To mitigate supply chain disruption, firms diversify supplier bases across regions and tiers, embrace nearshoring or friendshoring when sensible, and design resilient logistics strategies that combine multi-modal options and proactive routing. This network-centric approach reduces bottlenecks, shortens lead times, and keeps customer service levels intact even when one node falters.
Technologies such as cloud platforms, ERP systems, and AI-enabled analytics are no longer optional; they are essential for modern economy logistics. These tools provide real-time visibility and scenario planning that make risk management in supply chains actionable. Organizations can monitor OTIF, forecast accuracy, and recovery timelines, measure resilience, and translate insights into governance and supplier collaboration that sustains performance during shocks.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does supply chain resilience integrate risk management in supply chains to protect global supply chains against disruption?
Supply chain resilience blends proactive risk management with real-time visibility and agile execution to anticipate disruptions and minimize impact across global supply chains. Core elements include preparedness, end-to-end visibility, diversified supplier bases, flexible capacity, and rapid decision-making. Practically, use digital tools such as analytics and digital twins, strengthen supplier collaboration, and run scenario planning to adjust sourcing, production, and logistics in time. KPIs like OTIF, cycle time, and recovery time objective (RTO) help measure readiness and recovery performance.
What resilience strategies in supply chains are most effective for mitigating supply chain disruption in the modern economy logistics landscape?
Effective resilience strategies focus on visibility, diversification, and rapid response. Key actions include end-to-end mapping with real-time data, nearshoring or friendshoring where appropriate, strategic safety stocks and modular inventories, flexible manufacturing, and resilient, multi-modal logistics. Strengthen supplier collaboration and risk-sharing contracts, and maintain governance with clear ownership and metrics. Track outcomes using service levels, OTIF, inventory turns, and disruption recovery time.
| Theme | Key Points |
|---|---|
| What is supply chain resilience? | A holistic capability to anticipate, adapt, and recover from disruptions with minimal impact on performance; not a single tactic but a network-wide capability. |
| Core elements | – Preparedness: understanding vulnerabilities before they become failures. – Visibility: monitoring flows in real time, identifying bottlenecks, and acting quickly. – Flexibility: ability to switch suppliers, reroute shipments, adjust production/inventory without sacrificing service levels. – Speed: tempo of decision-making and execution—sense, decide, and act fast. |
| Business impact | Resilience affects cost structures, service quality, innovation, and competitive advantage; requires balancing redundancy with lean operation. |
| Risk drivers | – Demand volatility and forecasting uncertainty – Supplier concentration and single-sourcing – Geographic and geopolitical exposure – Infrastructure and climate risk – Cyber and data integrity risk – Transportation bottlenecks |
| Strategic approaches | – End-to-end visibility: map the network; use real-time data, digital twins, and AI analytics – Diversified supplier bases – Nearshoring and friendshoring where appropriate – Inventory optimization with strategic buffers – Flexible manufacturing and modular design – Resilient logistics strategies – Supplier collaboration and risk-sharing |
| Technology & data | Digital tools (cloud platforms, ERP, advanced analytics, AI) enable granularity and speed; real-time dashboards support scenario planning and stress testing; focus on data quality, interoperability, and governance. |
| Global interconnectedness | Global supply chains offer efficiency but increase exposure; resilience requires a network-centric view with cross-functional teams, shared metrics, and collaborative risk management. |
| Measuring resilience | Track leading indicators and outcomes: service level, OTIF, forecast accuracy, plus resilience metrics like RTO, cycle time variability, fill rate under stress, inventory turns under volatility, supplier disruption exposure, and TCO. |
| Case studies & lessons | COVID-19 showed cascading disruptions; lean models can be fragile without redundancy. Successful firms blend lean with redundancy, protecting margins and trust; resilience investments can reduce downtime and preserve customer relationships. |
| Cost vs resilience | Redundancy and safety stock raise carrying costs, but resilience yields value through reduced downtime, better service, and market share during disruptions; quantify value and align with risk appetite. |
| Policy, governance & the future | Governance should embed resilience in enterprise risk management with clear ownership and regular scenario exercises; collaborate with suppliers and industry groups; policy can invest in infrastructure and data sharing; future trends include autonomous tech and smarter regulation. |
Summary
Supply chain resilience is a dynamic capability essential to navigating modern uncertainty. By combining proactive risk management with agile, data-driven execution, organizations can navigate volatility, withstand disruptions, and emerge stronger after shocks. The most resilient networks balance efficiency with redundancy, maintain visibility and speed, and weigh short-term costs against long-term value. As global supply chains evolve, resilience remains a strategic differentiator that helps firms meet commitments, satisfy customers, and sustain growth even when the unpredictable occurs.