open source software has transformed how teams build, deploy, and iterate on technology, delivering transparency, collaboration, and rapid innovation. As organizations scale, they leverage OSS to accelerate development and reduce duplication of effort. This openness enables access to a vibrant community of open source software tools and frameworks. This reality brings licensing, governance, and security considerations that must be managed to sustain trust and reliability. This article highlights open source software benefits, explains open source software risks, and presents best practices open source software, along with guidance on open source licensing and open source security.
A different lens on this topic is community-driven software development, where source-available projects invite code reviews, collaboration, and collective responsibility. In this frame, teams evaluate licensing terms, governance models, and security implications as part of a transparent software ecosystem. By tracing dependencies, SBOMs, and risk signals across the software supply chain, organizations can anticipate issues before they impact production. Adopting this perspective helps align engineering culture with governance, risk management, and ongoing security practices. Together with the earlier discussion, it sets the stage for implementing robust practices for licensing, governance, and security within open source initiatives.
Open Source Software: Benefits, Risks, and Governance
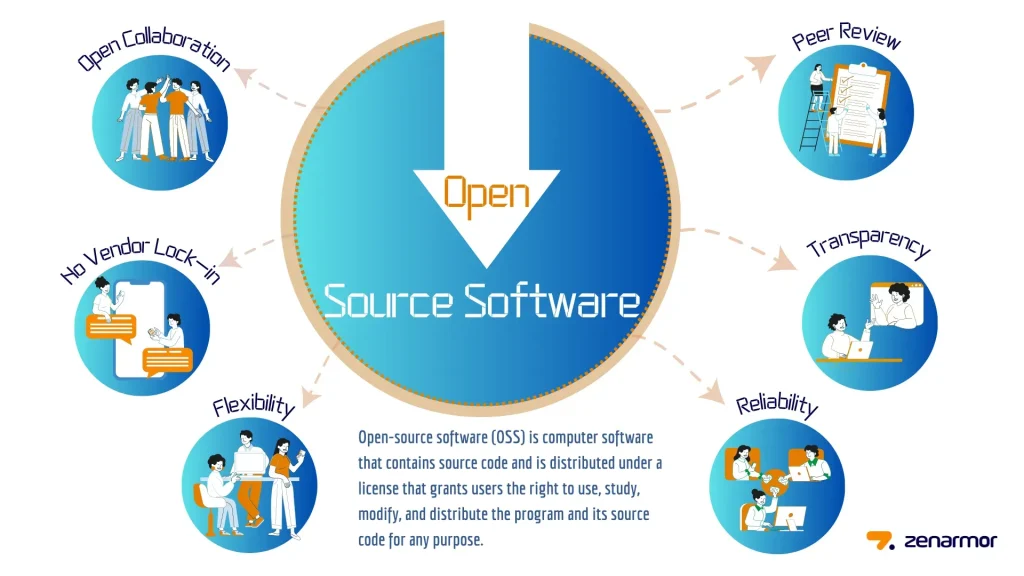
The open source software benefits include reduced costs, rapid iteration, and flexible customization. By eliminating licensing fees and enabling reuse of existing components, teams can redirect resources toward integration, experimentation, and value delivery. Access to the source code and a vibrant community also accelerates bug fixes and allows tailoring software to exact workflows, supporting faster time-to-value.
However, with benefits come the open source software risks that demand disciplined governance. Security and reliability concerns arise when maintenance lags, dependencies are unmanaged, or patches are delayed. Understanding open source licensing is essential to stay compliant and avoid unexpected legal exposure, while robust dependency management and SBOM practices help control risk. A governance program anchored in best practices open source software ensures teams can scale OSS responsibly while preserving speed.
Open Source Licensing and Security: Implementing Best Practices for OSS
Navigating the licensing landscape is critical for risk management. The open source licensing terms of MIT, Apache, GPL, and others shape how code can be used, modified, and redistributed in products. A clear understanding of licensing helps reduce legal risk while aligning with business goals. Beyond compliance, this awareness supports open source security by revealing potential supply chain vulnerabilities tied to specific licenses and components.
To operationalize, teams should adopt best practices open source software focusing on the software supply chain: maintain an up-to-date SBOM, integrate automated license scanning, perform vulnerability management, and apply patch cadences to critical dependencies. Open source security should be treated as a core aspect of software security, with defense-in-depth, container scanning, software composition analysis, and incident response planning. By combining licensing awareness with proactive security measures, organizations can realize the full value of OSS while mitigating risk.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the open source software benefits for organizations, and how can teams maximize these benefits?
Open source software benefits include lower costs, greater flexibility, faster innovation, transparency, and a vibrant community that accelerates development. To maximize these benefits, implement best practices for OSS governance, maintain a current OSS bill of materials (SBOM), and perform automated license scanning to align with open source licensing. Strengthen open source security by embedding OSS security into the development lifecycle, encouraging active community engagement, and ensuring interoperability across platforms.
What are the main open source software risks, and what best practices open source software teams should follow to mitigate them (including licensing and security)?
Open source software risks include security and reliability concerns, licensing and compliance challenges, dependency management complexities, governance overhead, and supply chain risk. Mitigate them with best practices open source software: establish governance and an SBOM, maintain an up-to-date inventory and risk dashboards, implement automated license checks (open source licensing), and build a security program with vulnerability scanning and timely patching. Foster contributor engagement and training to sustain OSS health and embrace a security-first mindset for open source security.
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| What is Open Source Software? |
|
| Benefits of Open Source Software |
|
| Risks of Open Source Software |
|
| Best practices for Open Source Software |
|
| Open source licensing and security interplay |
|
| Real-world considerations and examples |
|
Summary
Conclusion