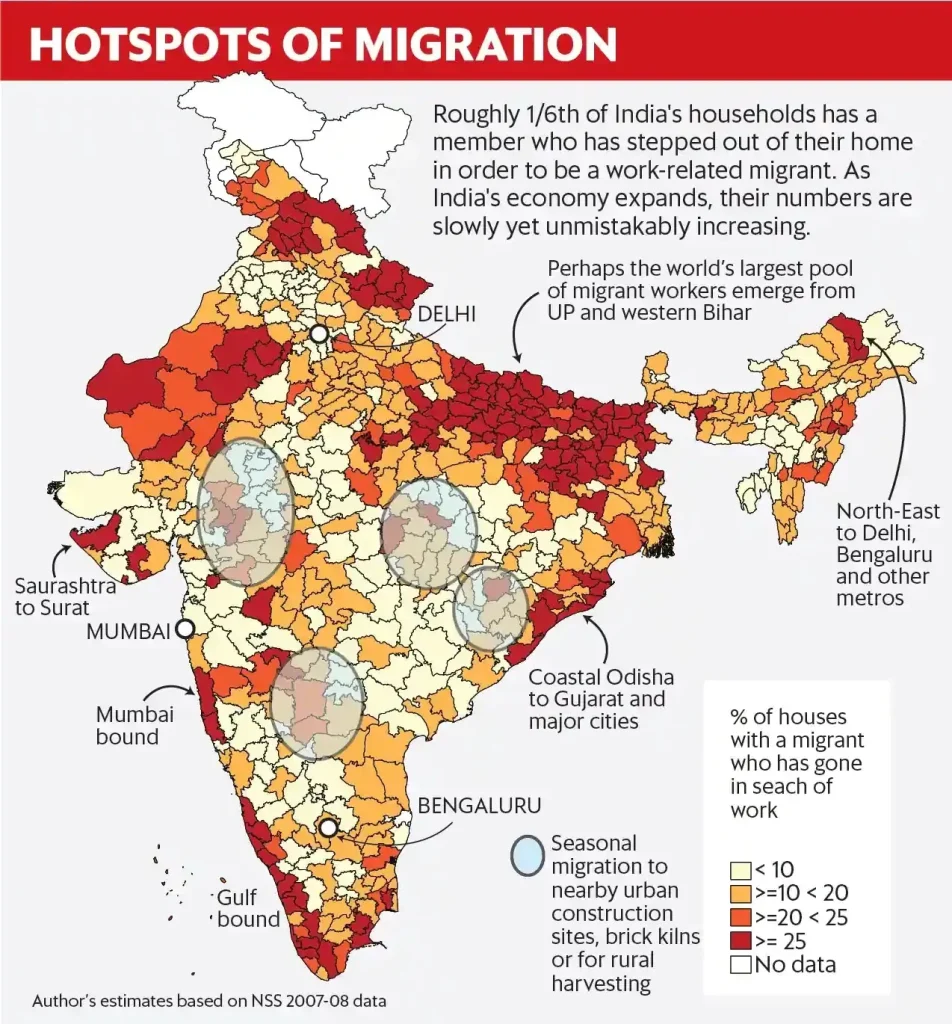
Migration challenges in India continue to pose significant obstacles to economic stability and growth as individuals flock from rural to urban areas. Despite the availability of a capable workforce in states like Bihar and Jharkhand, the disparity in employment opportunities drives many to predominantly developed regions such as Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu. Experts argue that without prompt agricultural reforms and bolstered infrastructure, the pressing issues related to workforce migration will remain unresolved. As highlighted in recent government initiatives, there is a clear call for creating more jobs in tier II cities to divert the influx towards major metropolitan areas. Addressing these migration challenges is vital not only for economic development but also for ensuring that the benefits of growth are more evenly distributed across the nation.
The hurdles of demographic shifts within India, characterized by rural-to-urban migration, highlight a larger systemic issue regarding labor distribution in the country. The trend, often referred to as workforce migration, has significant implications for regional development and the economy at large. As professionals and laborers seek better employment opportunities predominantly in urban areas, the imbalance causes strain on infrastructure and resources in major cities. To combat this, the government’s focus on enhancing tier II and III cities could pave the way for sustainable economic development while alleviating the pressures faced by densely populated urban centers. Therefore, addressing the underlying factors leading to agricultural stagnation and promoting diversified job creation is crucial for a more resilient workforce.
Understanding the Migration Trends in India
India’s migration landscape presents a complex picture, where the movement of individuals from less developed states like Bihar and Jharkhand towards more affluent regions like Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu reveals the inherent economic disparities. These trends are often driven by the search for better employment opportunities, as individuals seek to escape the pressing challenges of unemployment and underemployment that plague their home states. The stark differences in economic development across regions compound the growing workforce migration, creating a scenario where less favorable job markets in rural areas spur individuals towards urban centers.
Experts argue that addressing the significant workforce migration challenges in India necessitates a multifaceted approach involving agricultural reforms and infrastructure enhancements. These efforts aim to rejuvenate rural economies, ensuring that migration is a choice rather than an obligation for individuals. If tier II and III cities are adequately developed, they could potentially serve as alternative options for those migrating, thus balancing the economic opportunities across the nation.
The Role of Economic Development in Migration Patterns
Economic development plays a pivotal role in influencing migration patterns within India. The disparity in employment opportunities is a driving force behind the concentration of skilled labor in metropolitan areas, leading to a workforce migration that significantly favors urban over rural settings. As recruiters have pointed out, the focus on developing tier II cities is crucial in creating a more balanced job market, minimizing the rural-to-urban migration trend. Such development not only alleviates pressure on big cities but also fosters equitable economic growth across states.
Moreover, agricultural reforms are intrinsically linked to this economic development framework. Increasing productivity in agriculture can create new job opportunities in rural areas, therefore enabling local populations to remain and thrive without the need to migrate. The government’s initiative to boost employment by enhancing skills within the agricultural sector could have a substantial impact on retaining the workforce and revitalizing rural economies.
The Importance of Agricultural Reforms for Migration Mitigation
Agricultural reforms are crucial in curbing the incessant workforce migration from rural to urban areas. By focusing on increasing agricultural productivity and ensuring fair compensation for farmers, the government can help create sustainable employment opportunities within rural communities. As noted in the Economic Survey, the agriculture sector remains a dominant source of employment; therefore, reforming it could significantly alter migration patterns. .
With an increase in agricultural output and improved profitability, many young individuals currently migrating to urban centers for better job prospects may find attractive options within their own states. Implementing advanced farming techniques, improving irrigation systems, and providing access to markets are steps that could create a thriving agricultural sector and, in turn, reduce the necessity for migration.
Challenges of Workforce Migration Across States
The challenges of workforce migration in India are multifaceted. Variations in demand and supply for labor across different states create significant complications. For example, high demand for skilled workers in cities like Gujarat contrasts sharply with the surplus of labor available in states such as Bihar and Jharkhand. This imbalance results in an ongoing migration trend towards urban centers, where salaries and opportunities are perceived as more appealing.
Furthermore, the costs associated with relocation—ranging from physical moving expenses to potential cultural adjustments—add another layer of difficulty for workers considering migration. Recruiters emphasize that addressing these supply-demand disparities, coupled with meaningful interventions in infrastructure development and local job creation, is critical in overcoming the workforce migration challenges prevalent in India.
Boosting Employment Opportunities in Rural Areas
Creating employment opportunities in rural areas is vital to stemming the tide of migration to major cities. The government’s focus on generating job openings for marginal farmers and landless families is a step in the right direction, but it must also encompass a broad range of employment sectors. From supporting small-scale industries to developing rural entrepreneurship, there is a need for diverse job creation that appeals to the younger, educated workforce.
The promotion of vocational training and skill development programs specifically tailored for rural populations can prove beneficial in bridging the gap between rural skills and urban job opportunities. By encouraging local employment through enhanced skills training and infrastructure support, the government can foster sustainable economic growth and substantially reduce the migration pressures faced by urban centers.
Leveraging Tier II Cities for Economic Balance
The potential of tier II cities in India to absorb workforce migration and create economic balance cannot be overlooked. These cities, positioned as engines for growth, offer numerous advantages, including lower living costs and a burgeoning business environment. As companies establish operations in these areas, they create new employment opportunities suitable for the local population and returnees from metropolitan cities.
Recruiters suggest that the development of Global Capability Centres (GCCs) in tier II cities will not only alleviate the pressure on overburdened metropolitan regions but also stimulate local economies. Enhancing connectivity and infrastructure in these cities can attract companies seeking cost-effective operational locations, ensuring that skilled workers can find viable employment without needing to migrate to larger urban centers.
The Cost of Migration: Financial Implications for Workers
The financial implications of workforce migration present a critical hurdle for many Indian workers. The costs associated with relocating, whether for blue- or white-collar positions, can significantly affect the decision-making process. While earning potential is often higher in larger cities, the reality is that many workers may only see marginal differences in pay after accounting for the increased living expenses associated with urban life.
Moreover, the economic burden of migration affects not only individual workers but also families and communities as a whole. For those in states with limited economic opportunities, the allure of better salaries is enticing, but the financial strain during relocation can create obstacles that hinder long-term success. To truly mitigate the need for migration, a robust strategy targeting comprehensive economic development in rural and tier II cities is essential.
Aligning Skill Development with Market Needs
In the context of workforce migration, the alignment of skill development with market needs is paramount to ensuring that individuals are equipped for employment opportunities in both their home states and urban centers. Training programs must be informed by current job market demands, particularly in sectors that showcase growth potential, such as manufacturing, information technology, and services.
By investing in skill development and aligning it closely with regional economic needs, the government can enable workers to find fulfilling jobs without the compulsion to migrate. Bridging this skills gap will not only reduce migration pressures but also contribute to overall economic growth and stability across diverse regions of India.
Confronting Cultural Barriers in Migration
Cultural barriers present significant challenges for workers migrating from rural to urban areas. These challenges range from language differences to varying social practices that can impede a smooth transition for migrants seeking jobs in metropolitan environments. Overcoming these cultural hurdles is essential for institutions and organizations aiming to foster a more integrated workforce.
By promoting cultural sensitivity and awareness programs, employers can facilitate smoother transitions for workers from different backgrounds. Understanding the diversity and unique challenges faced by migrant workers can improve workplace integration, making it easier for them to navigate new environments while continuing their professional journeys.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main migration challenges in India affecting workforce migration?
Migration challenges in India predominantly revolve around the workforce supply-demand gap, wherein states like Bihar and Jharkhand have abundant labor but struggle to create sufficient employment opportunities. As economic development remains uneven, there’s a continued push towards major urban centers for better job prospects, which exacerbates the migration issues.
How do agricultural reforms influence migration challenges in India?
Agricultural reforms play a critical role in migration challenges in India by determining the economic viability of rural areas. If reforms lead to increased productivity and job creation in agriculture, it could make rural living more appealing and reduce the necessity for migration to cities in search of employment.
Are tier II cities equipped to handle the migration of workforce in India?
Tier II cities in India are seen as essential for easing migration pressures off tier I cities. Development of these cities is crucial to create job opportunities that can attract migrants from rural areas, thereby addressing migration challenges and fostering more balanced economic development.
What are the employment opportunities available for migrants in India?
Employment opportunities for migrants in India vary widely, with focus areas in manufacturing, IT, and services sectors. However, many young migrants gravitate towards urban jobs rather than agricultural roles, seeking better salaries and career prospects, which relates directly to the ongoing migration challenges.
How does economic development impact workforce migration in India?
Economic development significantly influences workforce migration in India by concentrating job opportunities in certain regions, particularly urban centers. While some states like Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu see an influx of skilled workers, regions lagging in economic growth struggle with high migration rates, leading to challenges in workforce distribution.
What is the government’s strategy to address migration challenges due to economic disparities?
The government’s strategy focuses on agricultural reforms and the promotion of employment opportunities in rural areas, suggesting that creating sufficient jobs can help ease migration. Furthermore, initiatives to establish Global Capability Centres in tier II cities are also part of the plan to balance workforce distribution and alleviate pressures on major cities.
How do employment trends affect migration patterns in India?
Employment trends indicate a significant shift towards urban centers as young, educated individuals seek formal jobs in sectors such as IT and manufacturing rather than agriculture. This urban migration pattern presents a critical challenge, as reliance on major cities for job creation continues to grow amidst uneven economic development.
What role does infrastructure development play in addressing migration challenges in India?
Infrastructure development is vital in addressing migration challenges in India since it enhances connectivity and creates a conducive environment for business. By improving transport and logistics in tier II and III cities, the government aims to foster local businesses and attract a workforce, thereby reducing the migration pressure on larger cities.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Migration Trends | Migration is primarily directed towards Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu from states like Bihar and Jharkhand. |
| Supply-Demand Gap | The workforce supply-demand gap exists due to uneven economic development across states, making migration a challenging issue. |
| Government Budget Objectives | The fiscal 2025-26 budget aims to create job opportunities in rural areas to reduce the necessity for migration. |
| Pressure on Urban Areas | There’s a growing pressure on large cities due to ongoing migration, emphasizing the need to develop tier II and III cities. |
| Cost of Relocation | Relocation costs for employees moving states can be significant, with variations in earnings influencing migration. |
| Sector Preferences | Young and educated individuals prefer formal employment opportunities in sectors away from agriculture. |
Summary
Migration challenges in India continue to pose significant obstacles as economic development remains uneven across states. Despite efforts from the government to create more employment opportunities in rural areas, the allure of bigger cities with higher earning potential persists. As a result, migration towards economically developed states like Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu remains a pressing issue that requires urgent attention and strategic planning.