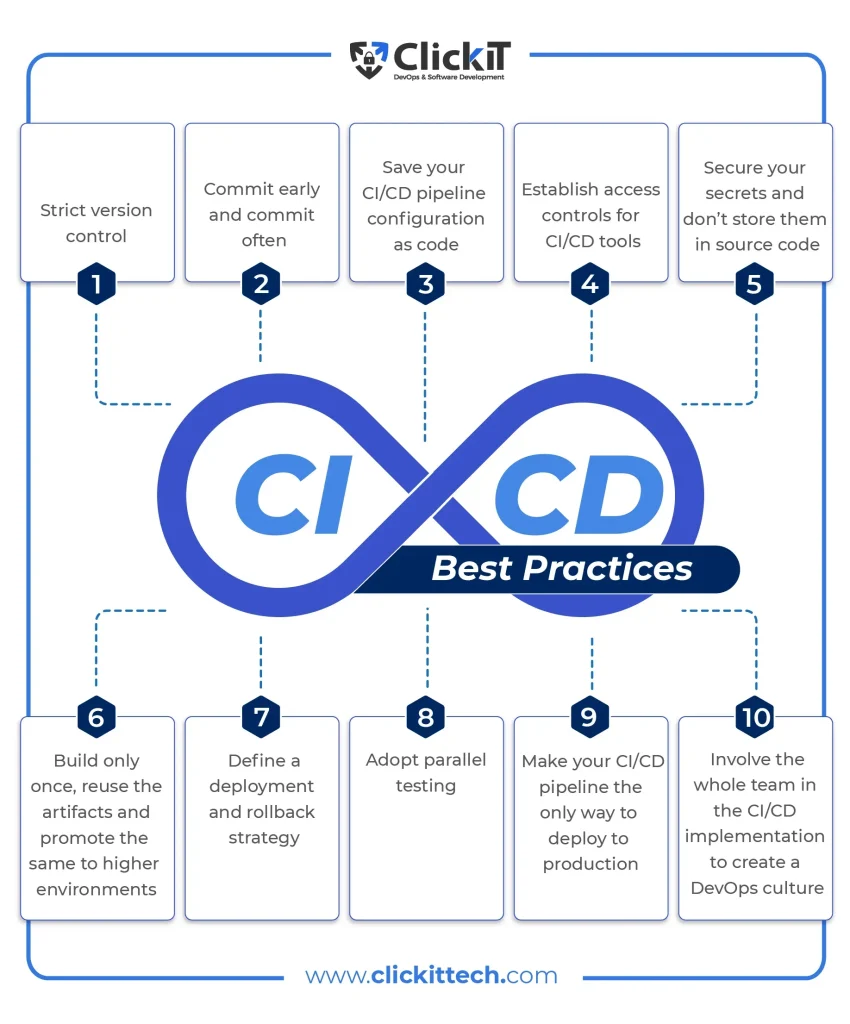
CI/CD best practices are the compass for reliable software delivery, guiding teams to ship features quickly without sacrificing quality, security, or maintainability, while aligning people, processes, and tools across the organization. In today’s fast-moving environments, teams rely on robust deployment pipelines to automate build, test, and release flows, supporting continuous integration and continuous delivery across multiple environments and teams, with scalable controls for compliance and auditing. This approach reduces manual toil, helps catch issues earlier, and enables deployments with confidence through repeatable processes, clear guardrails, automated rollback options, and measurable quality gates that illuminate risk before it reaches users. From source control and automated tests to secure artifact management and pipeline automation, DevOps best practices emphasize collaboration between developers, operators, quality assurance, security engineers, and product owners to sustain velocity without compromising safety. The result is faster feedback loops, higher quality software, and a predictable path from code to production that scales with teams, infrastructure, and evolving business goals.
Taking a broader view, this topic translates into the software delivery lifecycle and automated release workflows that move code from commit to production with confidence. A mature approach blends frequent code integration, automated testing, secure packaging, and automated deployments—collectively known as the build-to-release lifecycle. The focus shifts from individual steps to measurable outcomes like reduced lead time, fewer defects, and faster recovery, all achieved through a culture of collaboration and continuous learning. Related terms like deployment pipelines, continuous deployment, pipeline automation, and delivery orchestration capture the same idea from different angles in line with Latent Semantic Indexing principles. By adopting these concepts, teams create scalable, observable, and compliant software delivery practices that adapt as projects grow and environments evolve.
Designing Robust Deployment Pipelines with CI/CD Best Practices for Reliable Delivery
Robust deployment pipelines begin by aligning source control, automated builds, and comprehensive test suites into a single flowing process—the CI/CD assembly line. By embracing continuous integration and continuous delivery as core disciplines, teams shorten feedback loops, catch regressions earlier, and reduce drift across environments. Pipeline automation is the engine that makes this possible, turning code commits into repeatable, auditable releases with consistent quality, in line with DevOps best practices.
To realize CI/CD best practices, focus on artifact management, secure handling of credentials, and automated release coordination. Store immutable artifacts in a provenance-enabled repository, mirror production in test environments, and enforce governance gates before promotion. With strong rollback capabilities and clear rollback procedures, teams can recover quickly from incidents while maintaining velocity.
Observability, Security, and Governance in CI/CD-Driven Workflows
Observability serves as the compass for deployment pipelines, providing actionable metrics such as lead time, deployment frequency, change failure rate, and MTTR to guide improvement. By instrumenting the build, test, and release stages with metrics, logs, and traces, teams can detect drift or failures early and validate canary or blue/green deployments within a safe, automated pipeline.
Security and governance must be baked into every stage of the pipeline. Integrate SAST/DAST scans, enforce secret management and least-privilege access to CI/CD tooling, and maintain automated audit trails to support compliance objectives. When pipeline automation is paired with strong observability and policy controls, teams can ship faster without sacrificing reliability or security in deployment pipelines.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are CI/CD best practices for building robust deployment pipelines that enable continuous integration and continuous delivery?
Key CI/CD best practices for robust deployment pipelines include: 1) source control discipline with a clear branching strategy (e.g., trunk-based development) to ensure traceability; 2) automated builds and tests on every commit (unit, integration, and end-to-end) with production-like environments; 3) secure artifact management with immutable, provenance-tagged binaries; 4) integrated security checks (SAST, dependency checks) and vulnerability management; 5) secrets management with least-privilege access and rotation; 6) environment parity and configuration-as-code using IaC to reduce drift; 7) automated deployment strategies (blue/green, canary, rolling updates) and careful coordination with database migrations; 8) observability and telemetry across the pipeline (metrics, logs, traces); 9) governance and compliance gates where needed; 10) a culture of automation and collaboration (reusable templates, DevOps best practices); 11) explicit rollback plans and fast remediation; and 12) measuring success with key metrics like lead time, deployment frequency, change failure rate, and MTTR.
How can I apply pipeline automation and DevOps best practices within CI/CD to accelerate releases while maintaining quality and security?
Begin with pipeline automation by building modular, reusable stages for building, testing, packaging, security checks, and deployment. Apply CI/CD best practices such as trunk-based development and automated tests, and ensure artifacts are immutable and provenance-tracked. Use infrastructure-as-code to achieve environment parity, and integrate security early with SAST/DAST, dependency checks, and secret management with least-privilege access. Choose deployment strategies like blue/green, canary, or feature flags to minimize risk, and coordinate releases with schema changes. Invest in observability (metrics, dashboards, alerts) to monitor lead time, deployment frequency, change failure rate, and MTTR. Implement governance gates where appropriate, and maintain automated rollback procedures for quick remediation. Finally, foster a DevOps culture with cross-functional collaboration, reusable templates, and continuous improvement driven by measurable outcomes.
| Key Area | Summary |
|---|---|
| Source control and versioning | Central repository with clear branching; consistent versioning enables traceability, rollbacks, and audits. |
| Automated build and test suites | Each commit triggers a build with unit, integration, and end-to-end tests; high coverage reduces regressions; test environments mirror production. |
| Artifact management and reproducible builds | Artifacts stored securely in an immutable repository; reproducible builds ensure consistent outputs for audits and disaster recovery. |
| Static and security testing | Static analysis, SAST, and dependency checks integrated to catch vulnerabilities early and reduce the attack surface. |
| Secrets and credentials management | Secret management tools; disciplined access control; do not bake credentials into images or code; rotations and automated provisioning. |
| Environment parity and configuration as code | Infrastructure-as-code to provision environments consistently; reduces drift across dev, test, staging, and production. |
| Release strategies and deployment automation | Blue/green, canary, rolling updates, or feature flags; coordinate deployments with migrations to minimize outages. |
| Observability and telemetry | Instrument pipelines with metrics, logs, traces, and health checks; proactive monitoring enables rapid detection and continuous improvement. |
| Governance and compliance gates | Embed governance checks and audit trails; approvals captured automatically where appropriate while maintaining speed where possible. |
Summary
CI/CD best practices guide teams toward reliable software delivery by automating the journey from code commit to production, with built-in checks, tests, and guardrails that create fast, safe feedback loops. By standardizing pipelines, embracing environment parity, securing artifacts, and embedding observability and governance, organizations reduce risk, accelerate value delivery, and scale their software operations as teams and infrastructure grow. Implementing these practices fosters collaboration across development, operations, security, and product teams, delivering higher quality software, improved maintainability, and a resilient operating model.