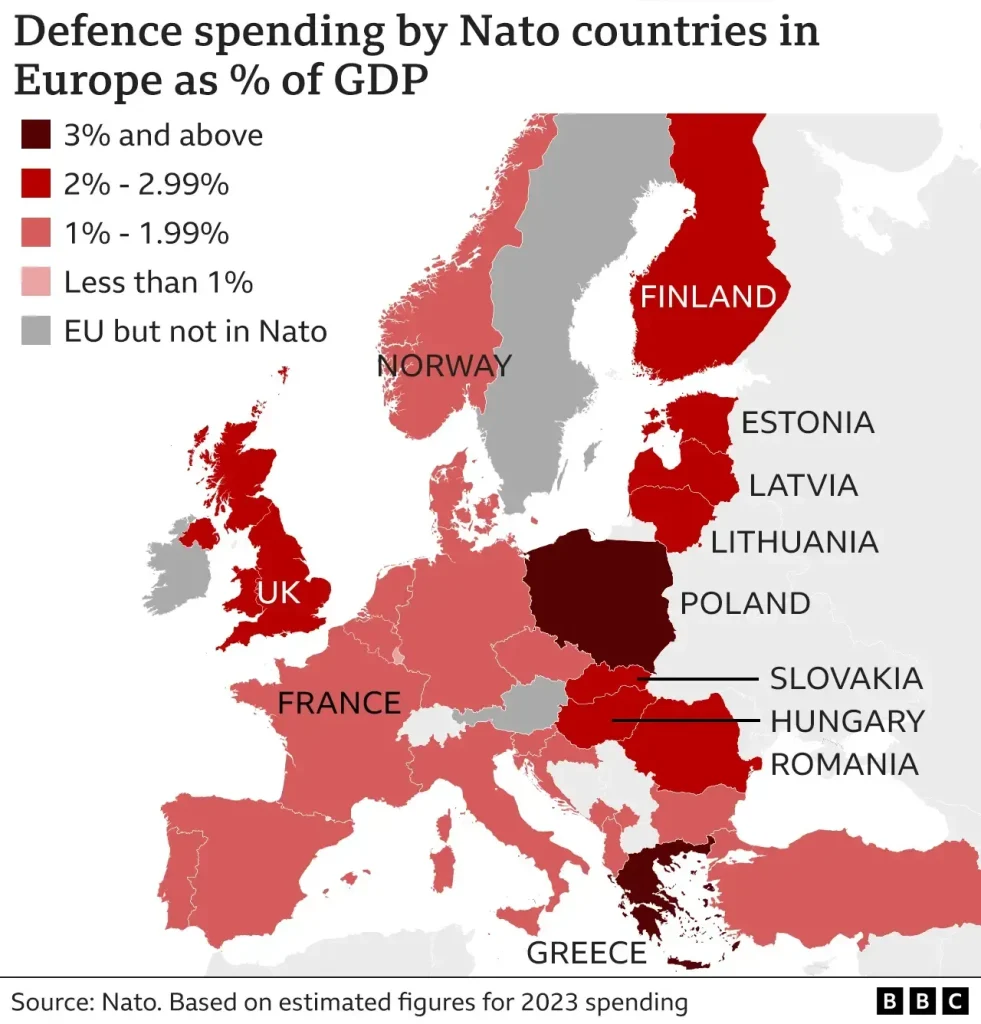
Greece NATO defense spending has emerged as a critical topic amid the current geopolitical climate, highlighting the nation’s strategic military priorities. Despite being known for its stunning landscapes and rich history, Greece ranks among the top defense spenders within NATO, allocating around 3.1% of its GDP towards national security in 2024. This substantial military budget is largely influenced by the ongoing tensions between Greece and Turkey, as both nations navigate a complex historical rivalry. Moreover, Greece’s position in the Mediterranean and its numerous islands necessitate a robust military presence to bolster its defense capabilities. As a result, understanding Greece’s military budget in the context of NATO defense expenditures reveals significant insights into regional security dynamics, particularly in light of rising geopolitical challenges.
The defense expenditures of Greece reflect a firm commitment to enhancing its military capabilities amidst ongoing geopolitical strains, particularly concerning its neighbor, Turkey. With a focus on securing the nation’s sovereignty, Greece’s military budget underscores the importance of preparedness in a volatile region. As tensions with Turkey continue to shape Greece’s defense strategy, the country’s financial allocations to its armed forces represent not only a defensive measure but also a statement of its strategic priorities within NATO. The investment in military capabilities serves to fortify Greece’s position among allied nations and enhance its engagement in broader defense discussions. Consequently, the landscape of defense spending in Greece is not merely an issue of finance but a critical aspect of its national security narrative.
The Significance of Greece’s NATO Defense Spending
Greece’s standing as a significant NATO defense spender is starkly illustrated by its dedication of approximately 3.1% of its GDP toward military expenditures in 2024. This metric not only places Greece among the upper echelon of NATO members investing heavily in defense but also underscores the geopolitical context in which it operates. The NATO alliance is increasingly focused on enhancing its collective defense posture, and Greece’s spending acts as a crucial barometer of its commitment. With increased tensions in the region, especially regarding Turkey, Greece’s military budget reflects a desire to reinforce its defense capabilities and ensure robust national security.
Moreover, Greece’s defense investments are not made in isolation. They resonate with the broader trends within NATO as member nations react to evolving security threats, especially following Russia’s assertiveness in Eastern Europe. The increase in NATO defense expenditures, now under discussion to potentially reach 5% of GDP for member states, positions Greece favorably among its allies. By maintaining high spending levels, Greece not only boosts its military capabilities but also enhances its negotiating power within NATO, fostering stronger alliances with key partners like the United States and France.
Greece-Turkey Relations and Military Budgeting
The military relationship between Greece and Turkey is a primary driver of Greece’s defense spending strategy. Historical conflicts and ongoing territorial disputes contribute to a climate of mistrust, compelling Greece to maintain a formidable military presence. Jacob Kirkegaard, a senior fellow at Bruegel, emphasizes the necessity for Greece to enforce a strong military stance, particularly on its numerous islands that are in close proximity to Turkey. These islands require substantial military resources and garrisons due to their strategic importance, which naturally inflates the national defense budget.
Furthermore, this precarious relationship has led to an environment where defense spending becomes synonymous with national identity and sovereignty. As George Tzogopoulos articulates, Greece’s commitment to high defense spending acts as a deterrent against any potential aggression while safeguarding its established borders and sovereignty claims. The geopolitical landscape of the Eastern Mediterranean adds layers of complexity, as Greece’s military preparedness is also aimed at countering any threats stemming from neighboring instabilities and Turkey’s assertive regional posturing.
Challenges in Greece’s Military Capabilities
Despite spending heavily on defense, Greece grapples with significant challenges that undermine its military capabilities. Experts point out that a considerable portion of Greece’s defense budget is allocated to foreign suppliers for advanced weaponry. While such investments are crucial, the lack of a robust domestic defense industry brings concerns over long-term sustainability. Without an indigenous industrial base, Greece could find itself overly reliant on external partners, affecting both its military readiness and strategic independence.
Additionally, the practical aspects of Greece’s military operations present hurdles that budgetary allocations cannot easily resolve. Many of Greece’s defense assets, such as tanks and tactical vehicles, are outdated and not optimized for modern warfare demands. There are also logistical challenges associated with maintaining military readiness across numerous, dispersed islands. Kirkegaard also points out that personnel training is another critical area for improvement. Adequate training programs must be established to ensure that military personnel can effectively operate equipment under varied conditions, ultimately bridging the gap between defense spending and operational effectiveness.
Greece’s Position in NATO and Future Prospects
Within NATO, Greece’s unwavering commitment to defense spending not only amplifies its voice but also solidifies its role as a strategic ally. As NATO consolidates its defense strategies in response to new threats, Greece’s military investments offer it a platform to influence broader coalition policies. By aligning its spending with NATO’s objectives, Greece can leverage its position to enhance its security guarantees—a priority given the ongoing challenges in its region. In essence, Greece’s role in NATO is as much about procurement and strategy as it is about geopolitical signaling to both allies and adversaries.
Looking ahead, the anticipated shift towards a 5% NATO defense spending target adds another layer of complexity. Experts suggest that while Greece might not fully meet the new requirements, its already substantial investment could provide flexibility to adapt as necessary. Greece has an opportunity to tailor its military strategies not only to bolster its defense against Turkey but also to contribute to NATO’s collective security efforts. As Athens navigates this evolving landscape, balancing domestic military needs with international obligations will be crucial for its future defense posture.
Greece’s Military Advancements and Strategic Investments
In its effort to modernize its military, Greece has made strategic investments in advanced weapon systems, reflecting a shift in focus due to changing geopolitical landscapes. Particularly in the wake of the Russia-Ukraine conflict, Greece has recognized the need to enhance its military capabilities through state-of-the-art technology. This includes upgrades to air and naval forces that are essential for safeguarding its territorial integrity and sovereign rights against potential aggressions.
However, while the emphasis on sophisticated weaponry is key, the path to becoming a military power requires comprehensive planning that includes bolstering domestic capabilities. Addressing the shortcomings in Greece’s defense industry and focusing on the development of indigenous production capabilities will not only enhance operational readiness but also provide economic benefits. This dual approach of investing in both advanced systems and domestic capabilities positions Greece to foster a more resilient military framework that can effectively address current and anticipated threats.
Navigating NATO’s New Defense Spending Targets
Amidst discussions surrounding heightened defense spending protocols within NATO, Greece faces unique challenges and opportunities. As alliance members deliberate increasing their expenditures to target levels of 5% of GDP, Greece’s strategic allocations will need to be assessed in terms of their feasibility. This proposed shift underscores the necessity for NATO countries to adapt to contemporary security environments, yet Greece must evaluate its position regarding economic constraints and its existing military commitments.
The evolving nature of warfare, influenced by hybrid threats and regional instability, necessitates a thorough examination of Greece’s current military budgeting priorities. The challenge will be balancing domestic expectations for military readiness with compliance to NATO’s collective defense obligations. By engaging actively in NATO discussions, Greece can advocate for tailored spending measures that reflect its unique strategic needs while still contributing to the collective security framework that underpins the alliance.
Geopolitical Implications of Greece’s Defense Spending
Greece’s high levels of defense spending have profound geopolitical implications, particularly in the context of its contentious relationship with Turkey. This financial commitment strengthens Greece’s military positioning and serves as a deterrent against regional aggression, showcasing the intersection of defense policy with national sovereignty and territorial integrity. As regional tensions continue to oscillate, Greece’s military readiness becomes not just a matter of national interest but also a strategic imperative that reshapes the dynamics within the Eastern Mediterranean.
Moreover, Greece’s investments signal to both allies and adversaries its resolve in the face of potential threats. The engagement of external powers like the United States and France further complicates the security landscape, establishing Greece as a pivotal actor in regional security discussions. As alliances evolve based on shared strategic interests, Greece’s role could expand, influencing trajectories of cooperation and confrontation within NATO and beyond.
The Economic Factors Behind Greece’s Defense Budget
Economic conditions play a crucial role in shaping Greece’s defense budget decisions. After enduring significant economic challenges in the last decade, including austerity measures, Greece’s renewed focus on military spending reflects a broader recognition of the necessity for a robust defense posture. Policymakers understand that national security is integral to economic stability, thus elevating military expenditure as a priority despite fiscal constraints. Balancing military obligations with economic viability demonstrates Greece’s commitment to securing its future.
While increased defense spending can bolster military readiness, it also poses risks to other sectors of the economy. Striking the right balance between investing in defense capabilities and ensuring social well-being remains a challenge for Greece. However, defense spending has the potential to stimulate local industries, enhance technological innovation, and create jobs—factors that contribute positively to the national economy. Such a multifaceted approach allows Greece to build a sustainable defense model that also fosters economic growth.
Enhancing Greece’s Military Partnerships in NATO
In light of its defense spending commitments, Greece is strategically enhancing its military partnerships within NATO. Collaboration with key allies not only amplifies its defense capabilities but also fosters a shared understanding of security needs in an increasingly complex geopolitical environment. Through joint exercises, training programs, and military exchanges, Greece is actively positioning itself to benefit from collective security mechanisms while ensuring its readiness to address any threats that may emerge.
Further, Greece’s military partnerships serve as a platform for sharing best practices and technological innovations relevant to modern warfare. This collaborative approach enhances interoperability among NATO forces and strengthens Greece’s position within the alliance. Building strong bilateral relationships with countries such as the United States, France, and other NATO members contributes to Greece’s overall defense strategy, ensuring that it remains a formidable player in both regional and international security arenas.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Greece’s NATO defense spending compared to other member countries?
Greece is one of NATO’s top defense spenders, allocating approximately 3.1% of its GDP to defense in 2024. This percentage ranks Greece among only four NATO allies—U.S., Poland, Latvia, and Estonia—who spent a larger portion of their GDP on defense due to heightened security needs, particularly in response to regional threats.
How do Greece’s military budget and Turkey’s military actions influence each other?
Greece’s military budget is significantly influenced by its tense relationship with Turkey. The ongoing territorial and historical disputes prompt Greece to maintain a robust military presence, especially on its islands close to Turkey’s coast, leading to substantial defense spending to assert its sovereignty and counter perceived threats.
Why is Greece’s defense spending considered high in relation to its military capabilities?
Despite its high defense spending, which focuses on sophisticated weapons acquisition, Greece does not possess strong military capabilities. The country lacks a robust domestic defense industry, and many of its military assets are outdated, which impacts operational efficiency and synergy among forces.
What role does Greece’s military spending play in its NATO relations?
Greece’s defense spending levels enhance its standing within NATO, providing geopolitical leverage and strengthening ties with key NATO allies like the U.S. and France. This relationship is particularly beneficial as these countries often supply military equipment to Athens and support its strategic interests in a complex regional environment.
How does Greece’s defense spending relate to tensions with Turkey?
Greece’s substantial defense spending is primarily a response to historical tensions and ongoing disputes with Turkey. The need to protect sovereignty and the potential threat posed by Turkish military policies necessitate high defense expenditures to ensure national security.
What challenges does Greece face despite its high defense spending?
Despite its significant military budget, Greece faces challenges such as an outdated inventory of equipment and insufficient training for personnel to operate large formations. Additionally, the geographical dispersion of equipment across islands complicates effective military deployment and readiness.
Is Greece viewed as a military superpower based on its defense spending?
No, Greece, while a top NATO defense spender, is not regarded as a military superpower. Experts highlight that high defense expenditures do not necessarily correlate with military strength, especially given Greece’s reliance on foreign arms and the challenges of an aging military infrastructure.
How does Greece’s military budget impact its security strategy?
Greece’s military budget is a crucial element of its security strategy, allowing the nation to prepare for various potential scenarios, particularly in light of regional instability. Strong defense spending serves as a deterrent against threats and reinforces Greece’s commitment to maintaining sovereignty in a volatile area.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| NATO Defense Spending | Greece is among the top defense spenders in NATO, allocating approximately 3.1% of its GDP to defense in 2024. |
| Tension with Turkey | The historical and ongoing tensions with Turkey drive Greece’s high military expenditure. |
| Military Superpower Status | Despite high spending, Greece is not considered a military superpower due to weaknesses in domestic defense capabilities. |
| Geopolitical Leverage | Greece’s defense spending enhances its geopolitical standing and strengthens relationships with powers like the U.S. and France. |
| NATO Spending Targets | The NATO target for defense spending may increase to 5%, which may be challenging for Greece to meet alongside its existing commitments. |
Summary
Greece NATO defense spending reflects the country’s commitment to maintaining its sovereignty amid regional tensions, particularly with Turkey. As one of NATO’s top defense spenders, Greece allocates a significant portion of its GDP to military expenditures, approximately 3.1% in 2024. This spending is largely driven by historical disputes and ongoing concerns regarding national security. While Greece’s investment in defense serves to enhance its geopolitical stature and strengthen alliances within NATO, experts argue that the nation still faces challenges in developing a robust domestic military capacity, underscoring the complex balance between expenditure and actual military effectiveness.